Editor
- FMA
- The Fabricator
- FABTECH
- Canadian Metalworking
Technology Spotlight: Production drill grinder
High-production drill grinder produces a completed drill in 20 seconds
- By Joe Thompson
- April 24, 2018
- Article
- Metalworking
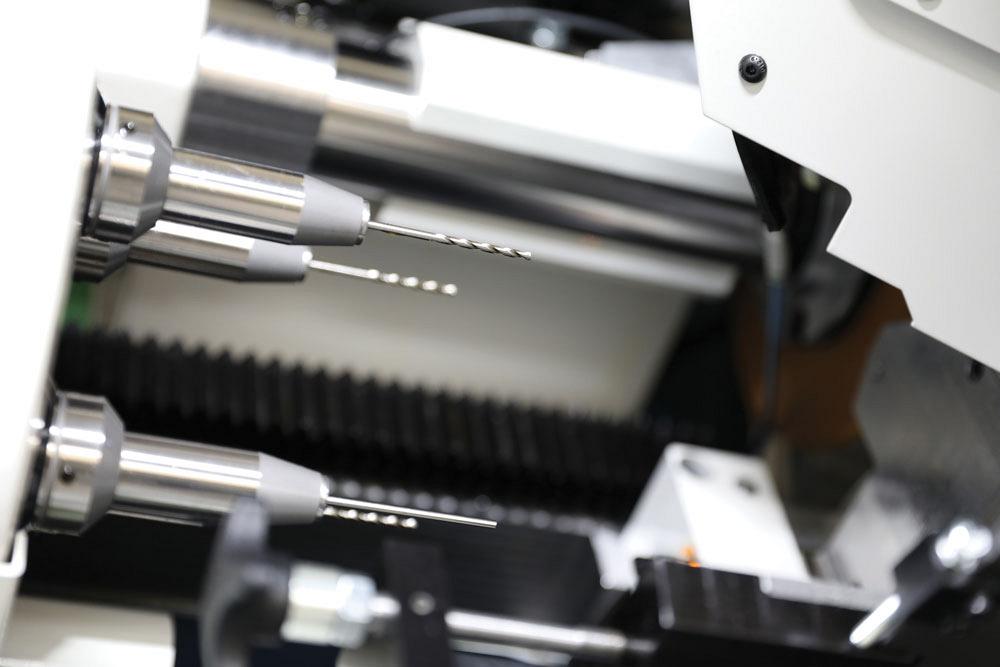

In one setup, drills from 0.8 to 4 mm dia. are formed from a blank and the machine grinds the flutes, relief, and point, producing a finished drill. Photo courtesy of ANCA.
Nearly 2 billion high-speed steel (HSS) drills are produced every year. To reduce production time and cost of these manufacturing mainstays, shops now can perform drill grinding on a single machine, eliminating multiple setups.
One such machine is the recently introduced ANCA FCP4 high-production drill grinder.
ANCA, Melbourne, Australia, manufactures CNC grinding machines and has offices in the U.S., U.K., Germany, China, Thailand, India, Japan, and Brazil, as well as a network of representatives and agents worldwide. The company’s CNC grinders are used for manufacturing precision cutting tools and components across numerous industries, including cutting tool manufacture, automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical.
Drill Production
The new drill grinder can produce HSS drills from 0.8 to 4 mm dia. on a single machine. In one setup, the drills are formed from a blank and the machine grinds the flutes, relief, and point, producing a finished drill.
“The high-volume commodity drill market is a new market for us, but is a great fit given our 40-plus years’ expertise in tool and cutter grinding,” said Grant Anderson, CEO of ANCA.
The new machine enables a complete drill to be manufactured every 20 to 25 seconds, a significant difference from how drills currently are produced, on two or three separate machines.
The CNC capability of this drill grinder also enables quicker changeover and reduces setup times, making the option of smaller production runs viable. Changing the drill size during production typically takes several hours and creates needless waste with scrap, the company states.
“We think we can bring a huge benefit to the industry [because] up until now there is little competition or product choice for volume manufacturers of HSS drills. Drill manufacturers are typically restricted to using machines that are old and CAM-operated. With older machines wearing out, there are currently very few options for upgrading or improving their capabilities,” said Anderson.
This machine is CNC-operated and has eight axes, using a principle similar to a Swiss automatic machine in which a multi-turret undertakes several operations simultaneously. The machine uses an ANCA Motion CNC system, including AM5C drives, AMI5000 Touchpad, Commander, AMCore, and MotionBench.
According to ANCA, the accuracy focus during the grinding process usually is on the drill’s runout specifications, height variation, and lip-to-lip distance. Low runout (less than 0.0002 in.) is the goal because the drill produces a rounder hole and resists wandering.
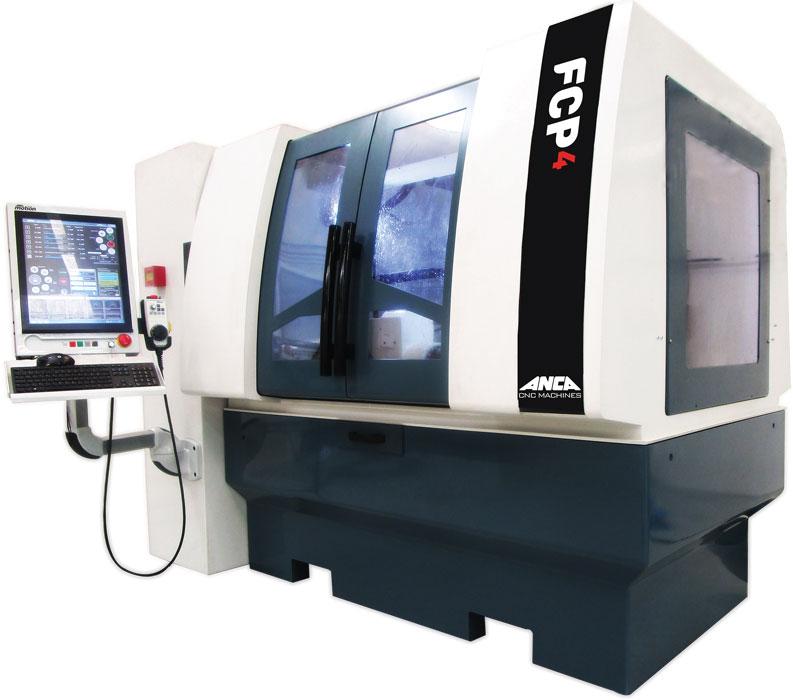

The ANCA FCP4 uses machining principles that are similar to a Swiss automatic machine, which uses a multi-turret to perform several operations simultaneously. Photo courtesy of ANCA.
“We listened to our customers who, in this market, faced a lack of choice and responded to their needs to develop our own solution. With our extensive market knowledge and research and development capabilities, I am confident this new machine will be well-received and unleash a whole new world of possibilities for our customers,” said Simon Richardson, FCP4 product manager.
This drill grinder has full CNC grinding and dressing capabilities, and flute shape can to be adjusted by the CNC and form dressed on the machine.
Editor Joe Thompson can be reached at jthompson@canadianmetalworking.com.
ANCA, www.anca.com
About the Author

Joe Thompson
416-1154 Warden Avenue
Toronto, M1R 0A1 Canada
905-315-8226
Joe Thompson has been covering the Canadian manufacturing sector for more than two decades. He is responsible for the day-to-day editorial direction of the magazine, providing a uniquely Canadian look at the world of metal manufacturing.
An award-winning writer and graduate of the Sheridan College journalism program, he has published articles worldwide in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, pharmaceutical, medical, infrastructure, and entertainment.
Related Companies
subscribe now


Keep up to date with the latest news, events, and technology for all things metal from our pair of monthly magazines written specifically for Canadian manufacturers!
Start Your Free Subscription- Trending Articles
Sustainability Analyzer Tool helps users measure and reduce carbon footprint
GF Machining Solutions names managing director and head of market region North and Central Americas

Mitutoyo updates its end-user portal
Enhance surface finish with high-speed machining

Portable 3D scanners offer adjustable scanning distance, advanced volumetric accuracy

- Industry Events
Automate 2024
- May 6 - 9, 2024
- Chicago, IL
ANCA Open House
- May 7 - 8, 2024
- Wixom, MI
17th annual Joint Open House
- May 8 - 9, 2024
- Oakville and Mississauga, ON Canada
MME Saskatoon
- May 28, 2024
- Saskatoon, SK Canada
CME's Health & Safety Symposium for Manufacturers
- May 29, 2024
- Mississauga, ON Canada















